Explore the evolution of electronic medical record systems, key innovations in 2025, and why staying updated is crucial for healthcare professionals and students.
EMR Trends at a Glance – 2025:
|
What Is an Electronic Medical Records System?
If you’re wondering “what is an electronic medical record?” — the term refers to digital systems that store patient data such as diagnoses, medications, lab results, imaging, and visit notes. These platforms have replaced traditional paper charts in most hospitals and clinics.
Today, electronic medical record systems (EMRs) are central to the healthcare experience, enabling better care coordination, fewer errors, and real-time access to a patient’s medical history.
According to the reports by the National Library of Medicine, 96% of U.S. hospitals now use certified EMRs, and with rapid advances in cloud computing and artificial intelligence, the next generation of EMRs is already here.
Let’s explore the biggest changes shaping medical electronic records in 2025.
1. AI-Powered Documentation and Virtual Scribes
One of the most groundbreaking changes to EMRs is the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI). In 2025, doctors no longer spend hours typing notes—voice-enabled assistants and virtual scribes transcribe conversations into structured records using Natural Language Processing (NLP).
- Voice-to-text features reduce documentation time
- AI decision support helps detect drug interactions or alert providers to sepsis risks
- Automation handles repetitive tasks like billing code suggestions or follow-up reminders
These innovations enhance data quality and reduce burnout—two major pain points of traditional EMRs.
2. Cloud-Based EMRs and Remote Accessibility
Traditional hospital electronic medical records relied on local servers. Today, many providers have moved to cloud-hosted EMRs, enabling anytime, anywhere access.
Benefits of Cloud EMR Systems:
| Traditional EMRs | Cloud-Based EMRs |
| On-site only | Accessible from any device |
| High IT maintenance | Vendor-managed updates & backups |
| Expensive infrastructure | Cost-effective subscription pricing |
Whether in a rural clinic or a telehealth call, cloud platforms let healthcare professionals update charts and review histories in real-time—boosting collaboration and continuity of care.
3. Telehealth & Wearable Device Integration
The pandemic accelerated telehealth, and EMRs are catching up fast. In 2025, healthcare electronic records will fully support:
- Telehealth visit documentation
- Integration with wearables and home monitoring devices (e.g., smartwatches, glucometers)
- Chronic care tracking from patients’ homes
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) now feeds continuous data—like blood pressure or oxygen levels—into EMRs, giving care teams real-time insights and enabling preventive interventions.
4. FHIR & Interoperability: EMRs That Actually Talk to Each Other
For years, one of the biggest complaints about EMRs has been the lack of interoperability—the inability for systems to share data.
That’s changing.
- FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) is a new standard that lets EMRs communicate effortlessly
- Nationwide frameworks like TEFCA are connecting regional systems
- Patients can now access their entire health record via mobile apps using open APIs
The goal is simple: your health data should follow you, no matter which provider or state you visit.
5. EMRs and Patient Empowerment
Today’s patients expect instant access to their health information—and EMRs are evolving to meet that demand.
Modern patient portals allow users to:
- View lab results and clinical notes
- Send secure messages to providers
- Complete pre-visit forms and health questionnaires
- Receive medication reminders or appointment alerts
This is a shift from provider-only records to interactive, patient-centered EMRs.
Also, platforms now support Personal Health Records (PHRs), allowing patients to download their data, track conditions, and even contribute home-collected data to their charts.
6. Stronger Data Security and Electronic Medical Records Law Compliance
With increased digital access comes a need for airtight data privacy and security. In 2025, EMR platforms are implementing:
- End-to-end encryption
- Multi-factor authentication for all users
- Audit trails for every change made to a record
When can a medical record be changed?
Legally, medical records can only be amended with proper documentation. Every correction must be time-stamped and include the original entry for transparency, as per HIPAA guidelines.
How is a correction made to an electronic health record?
EMRs allow authorized personnel to add an amendment rather than overwrite original data. This ensures medical, legal, and billing integrity is preserved.
Technologies like blockchain are also gaining traction to ensure immutability, with tamper-proof logs of every access or edit—supporting compliance with electronic medical records law.
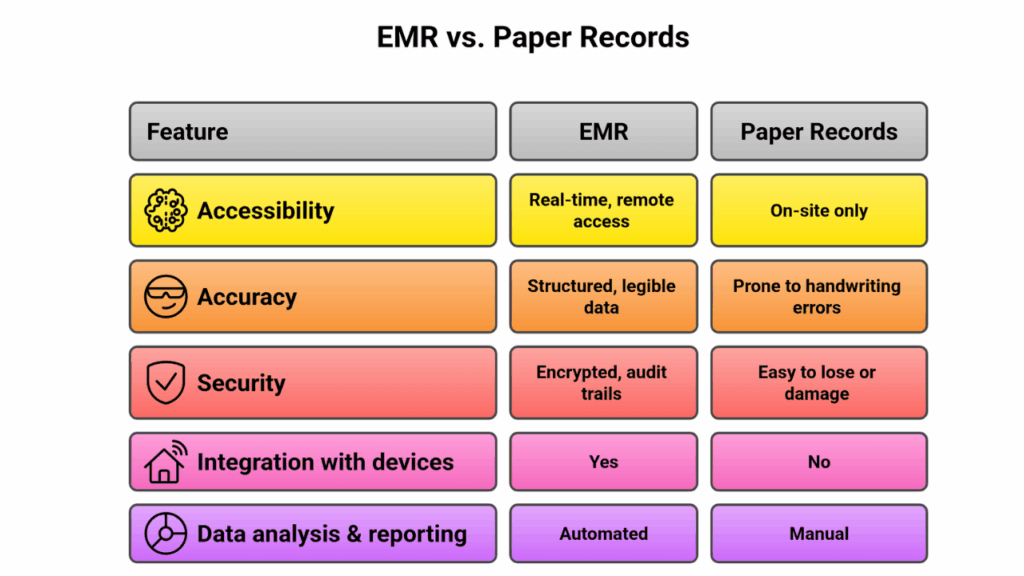
7. EMR vs. Paper Medical Records: Still a Debate?
Some skeptics still ask whether EMRs are truly better than the old pen-and-paper method.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | EMR | Paper Records |
| Accessibility | Real-time, remote access | On-site only |
| Accuracy | Structured, legible data | Prone to handwriting errors |
| Security | Encrypted, audit trails | Easy to lose or damage |
| Integration with devices | Yes | No |
| Data analysis & reporting | Automated | Manual |
The verdict is clear: EMRs outclass paper records in accuracy, efficiency, and patient outcomes. The key is ensuring healthcare workers are properly trained to use them.
8. A Look Back: When Was the First Electronic Health Record Created?
The first electronic health record systems emerged in the 1960s, developed by academic and government institutions like the Mayo Clinic and VA hospitals.
But widespread adoption began only in the 2000s, after government incentives under the HITECH Act encouraged providers to digitize records.
Understanding the history helps us appreciate the incredible progress made—and where we’re heading next.
Challenges Ahead (And How We’re Solving Them)
Even in 2025, EMRs still face roadblocks:
- Legacy systems slow down interoperability
- User frustration from clunky interfaces
- Data overload and alert fatigue
- Privacy concerns as third-party apps integrate with EMRs
The good news? Industry-wide initiatives and emerging tech (like AI interfaces, blockchain logs, and user-driven design) are actively addressing these issues.
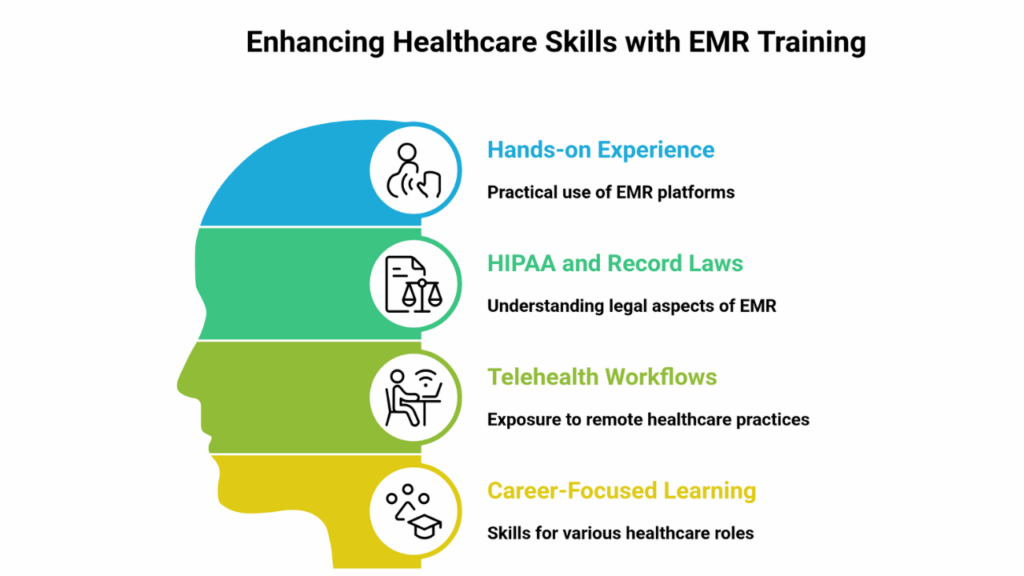
Why Training Matters: Learn EMRs the Right Way
Knowing how to use EMRs effectively is just as important as the tech itself.
That’s why electronic medical records programs—like those at CCI Training Center—are essential for modern healthcare professionals.
CCI’s EMR training includes:
- Hands-on experience with real-world EMR platforms
- Understanding HIPAA and record correction laws
- Exposure to telehealth workflows and cloud documentation
- Career-focused learning for clinical and administrative roles
Whether you’re a medical assistant, billing specialist, or future healthcare IT professional, strong EMR skills give you an edge in the job market.
Conclusion: The Future Is Digital—Are You Ready?
Electronic medical record systems have evolved from basic digital charts to powerful, AI-driven care platforms. They’re smarter, safer, more connected—and they’re only getting better. Whether you’re new to the healthcare field or looking to upskill, now is the time to embrace EMRs and their exciting future.
Ready to build in-demand skills in healthcare technology?
Learn how to navigate modern EMR systems with confidence—whether you’re starting your healthcare career or leveling up your role.
Explore CCI Training Center’s Electronic Medical Records Program and take the next step toward a digital healthcare future.
Stay current. Get trained. Improve patient care.
Program Offered
- Pharmacy Technician Training
- Online Medical Assistant
- Medical Billing and Coding Specialist Program
- Cloud Computing Technician Training
- Computer Network Technician
- Business and Accounting
- Radiology Technician Training
- Medical Assistant Program
- Computer Support Technician
- Cybersecurity Program
- Virtual Assistant Training

This article is written by
Share this article
Frequently Asked Questions FAQ's
What is the difference between EHR and EMR?
An EMR (Electronic Medical Record) is a digital version of a patient’s chart within one provider’s system. An EHR (Electronic Health Record) goes further—it’s designed for sharing across systems and providers, offering a broader view of a patient’s history.
How is a correction made to an electronic health record?
Corrections are made through an addendum, which preserves the original entry while allowing updates. This process is governed by HIPAA and documented through audit logs.
When can a medical record be changed?
Medical records can be changed only by authorized personnel, and only for legitimate reasons—such as correcting an error or adding missing info. Changes must be timestamped and tracked.
What are the best electronic medical records programs for beginners?
Programs that offer:
- Real software simulations
- Compliance training
- Hands-on labs
Like the one offered at CCI Training Center, these are ideal for beginners entering healthcare or administrative roles.
Program Offered
- Pharmacy Technician Training
- Online Medical Assistant
- Medical Billing and Coding Specialist Program
- Cloud Computing Technician Training
- Computer Network Technician
- Business and Accounting
- Radiology Technician Training
- Medical Assistant Program
- Computer Support Technician
- Cybersecurity Program
- Virtual Assistant Training

This article is written by
Share this article
Related Articles