Medical Law & Ethics Training in the State of Texas
The 20th century marks the beginning of modern healthcare. After more than 100 years, a great deal is known about the human body that was not known in the last 10,000 years.
With so much at stake, medical laws and ethics have become the backbone of the medical field. Ensuring patient safety, confidentiality, and quality care requires strict adherence to legal and ethical guidelines.
Many U.S. states mandate practice in accordance with medical norms. In Texas, these norms are regulated by the Texas Medical Board (TMB), aligning with the core principles of medical ethics.
Laws and ethics are essential for healthcare professionals to maintain the integrity of healthcare practices. Violations may result in:
- Legal consequences
- Loss of licensure
- Compromised patient trust
This blog aims to educate future healthcare professionals and interested medical students on the significance of medical law and ethics training in Texas.
Let’s explore key regulations and ethical dilemmas to help healthcare practitioners navigate complex medical situations with professional integrity.
Importance of Medical Laws & Ethics for Healthcare Practitioners
Healthcare professionals often face legal and ethical challenges such as patient confidentiality and end-of-life decisions.
Such situations require a firm grounding in both law and ethics:

Texas-specific legal obligations include:
Essential Texas Laws for Fair Medical Practices
01. Texas Medical Board (TMB) Regulations
The TMB regulates ethical medical practice in Texas, including licensing and disciplinary actions for physicians and healthcare providers.
Licensing Requirements
- Proper education, exams, and background checks
Disciplinary Actions
- Penalties for malpractice, fraud, or unethical behavior
Continuing Medical Education (CME)
- Mandatory ethics training for license renewal
02. Texas Advance Directives Act
When treatment is ineffective, the Texas Advance Directives Act (1999), also called the Futile Care Law, addresses medical futility.
| Medical Futility – Medical interventions unlikely to benefit the patient significantly, based on success probability and benefit quality. |
The ethics committee reviews such cases where continued care may go against medical judgment.
Case Study
Patient Mr. J (82 years old) had renal failure, and treatments were proving ineffective. The Texas Advance Directives Act resolved the matter ethically, balancing autonomy and medical judgment.
03. HIPAA Compliance in Texas
HIPAA Privacy Rule mandates:
- Secure handling of Protected Health Information (PHI)
- Patient consent before sharing records
- Fines up to $50,000 per violation for breaches
Medical Practice’s Ethical Dilemmas in The State of Texas
01. End-of-Life Care
When health declines and recovery is unlikely, medical staff and ethics committees face difficult ethical decisions.
Ethics Vs. Law Conflict
Often, legal and ethical views may clash. For example, under Texas law, hospitals can withdraw life-sustaining treatment with a 10-day notice after ethics review—potentially against a professional’s moral views.
02. Informed Consent & Patient Autonomy
Doctors must explain risks and benefits before treatments. Failure to do so can result in malpractice lawsuits.
03. Public Safety Vs. Confidentiality
“When should doctors break confidentiality?” This question arises in cases like:
- Gunshot wounds
- Infectious disease reporting
Despite breaking confidentiality, Texas law requires reporting child abuse, elder abuse, and communicable diseases.
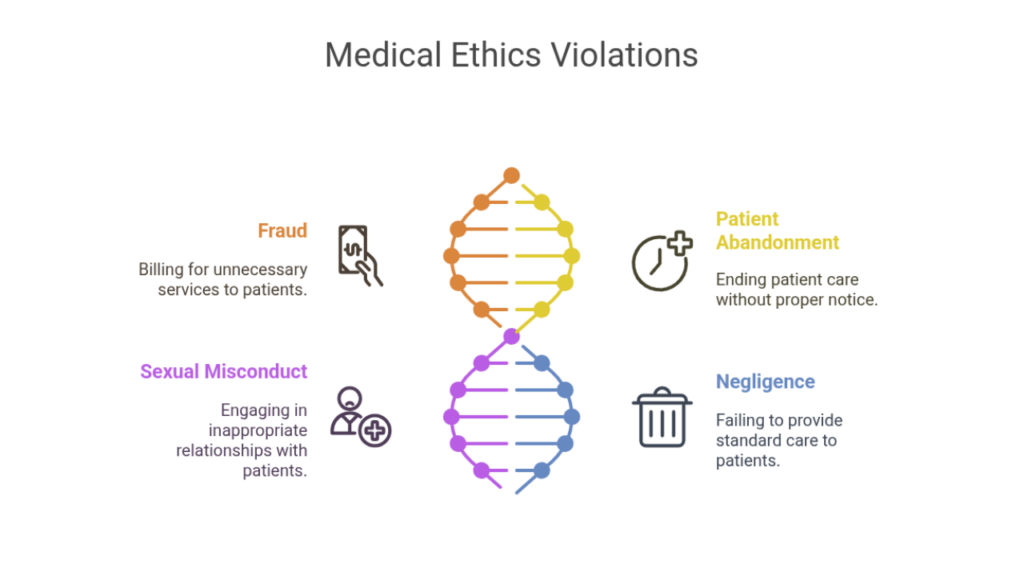
Strict Violations of Medical Ethics in Texas
The Texas Medical Board enforces penalties for unethical conduct.
Conclusion: Why Medical Law & Ethics Training is Non-Negotiable

Healthcare professionals in Texas must stay updated on changing laws and ethical practices.
Whether it’s HIPAA compliance, end-of-life decisions, or patient consent, this knowledge improves patient care and provides legal protection.


