How to Pay for Career Training: Financial Aid, Student Loans & More
Quick Summary
|
Are you considering career training but concerned about how to afford it?
You’re not alone. For many adults and recent graduates, the cost of education is one of the biggest barriers to advancing their careers. But the data make one thing clear: education pays off.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, workers with an associate degree earned a median of $1,099 per week — compared to just $930 for high school graduates. That difference adds up to nearly $9,000 more per year, along with a lower unemployment rate (2.8% vs. 4.2%).
The good news? With options like federal student loans, Pell Grants, financial aid student loans, and job training loans, career training is more affordable than most people realize — and the return on investment can be life-changing.
Financial Aid vs. Student Loans: What’s the Difference?
Not all financial aid is created equal. Some is “free money,” while other aid must be paid back over time. Understanding the differences will help you prioritize funding sources and borrow wisely.
- Grants & Scholarships → Free money you don’t repay.
- Work-Study → Earned aid through part-time work.
- Student Loans → Borrowed money, repaid with interest.
Key takeaway: Always maximize free aid before turning to loans.
Types of Financial Aid
To make sense of your options, it helps to compare different types of financial aid side by side. The table below highlights which funding sources require repayment and which ones don’t, along with who they’re best suited for.
Aid Type | Repayment Required? | Source | Best For |
Pell Grant | No | Federal Gov’t | Low-income students |
Scholarships | No | Schools, foundations, orgs | Merit or need-based awards |
Work-Study | No (earned pay) | Federal program via FAFSA | Students balancing study + part-time work |
Federal Student Loan | Yes | Dept. of Education | Most students need extra funding |
Private Student Loan | Yes | Banks, lenders | Students with funding gaps after FAFSA |
Federal Financial Aid for Career Training
Career schools like CCI Training Center are Title IV eligible, meaning students can apply for FAFSA-based aid.
Federal loans remain the most common source of career training financing because they combine accessibility with lower interest rates. Let’s review the four key types.
Types of Federal Student Loans
The table below outlines the main loan categories, interest rules, and key details so you can easily see how they compare.
Loan Type | Who Qualifies? | Interest Rules | Notes |
Direct Subsidized Loan | Undergrads w/ financial need | Govt pays interest during school | Best option for low-income students |
Direct Unsubsidized | All undergrads/grads | Interest accrues immediately | Most common loan for career training |
Direct PLUS Loan | Parents or grad students | Higher interest; requires a credit check | Covers costs not met by other aid |
Direct Consolidation | Borrowers w/ multiple loans | Not new money; combines existing loans | Used after school for simplified repayment |
2025–26 Federal Loan Rates:
- Subsidized & Unsubsidized (Undergraduate): 6.39%
- Graduate (Unsubsidized): 7.94%
- PLUS Loans (Parents & Graduate Students): 8.94%
FAFSA is your gateway. Use CCI’s FAFSA school code 040894 to apply.
Financial Aid for Career Training vs. College
- Myth: FAFSA only applies to 4-year universities.
- Fact: As long as your program is accredited and Title IV eligible, you can use federal student loans and grants for career training programs as well.
Many students don’t realize that accredited career schools like CCI Training Center qualify for the same aid options as colleges — often at a fraction of the cost.
Example:
- A CCI healthcare certification (~$10,000) may be fully funded by Pell + a small loan.
- A traditional university degree (~$40,000/year) leaves much larger debt gaps.
This difference explains why career schools can be a faster, smarter path for many students.
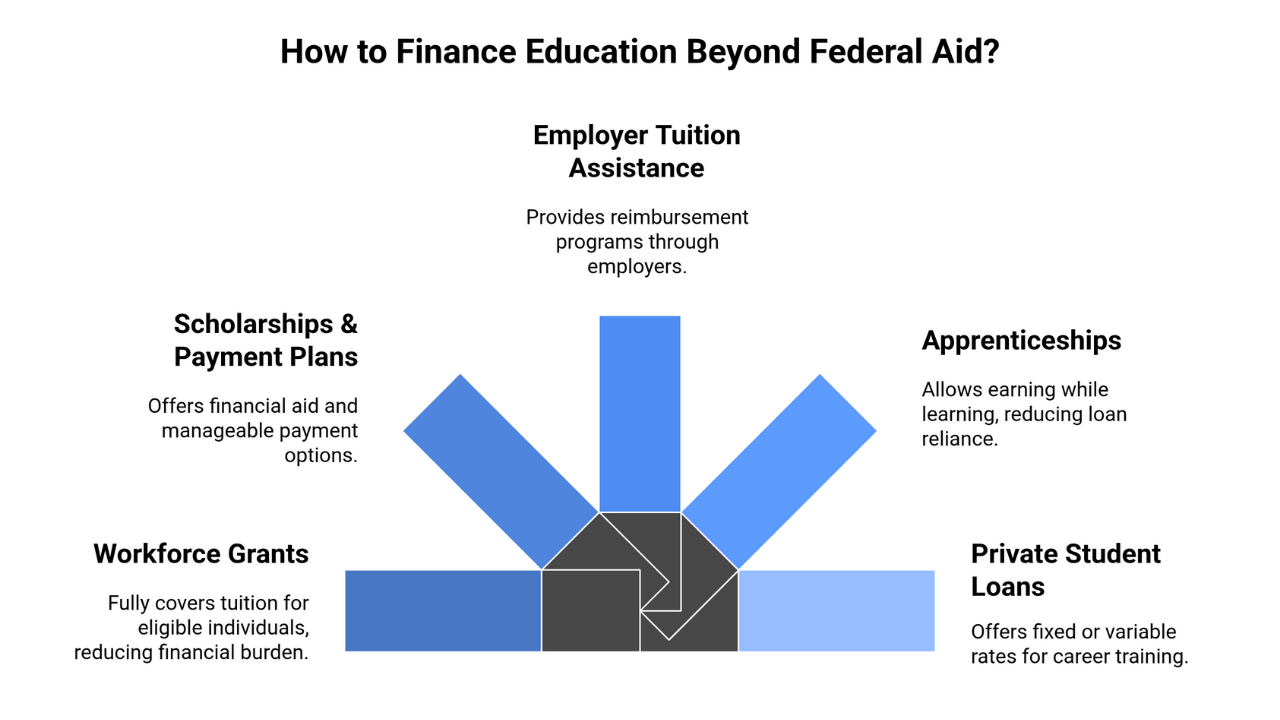
Beyond Federal Aid: More Options
While federal aid is often the foundation of education funding, many students combine it with additional resources to reduce borrowing and make career training more affordable.
Workforce Grants (WIOA)
CCI is an approved WIOA provider. Grants can fully cover tuition for laid-off workers, youth (16–24), or adults re-entering the workforce.
Scholarships & Payment Plans
- Director’s Scholarship available for qualifying CCI students.
- In-house payment plans (zero/low interest) spread tuition into manageable monthly amounts.
Employer Tuition Assistance
Amazon, Walmart, Starbucks, and even smaller employers often provide reimbursement programs.
Apprenticeships / Earn While You Learn
In fields like IT, healthcare, or trades, apprenticeships allow you to earn income while training, reducing reliance on loans.
Private Student Loans & Job Training Loans
When all else fails, banks and online lenders offer “career training loans.”
- Fixed rates = safer, predictable payments.
- Variable rates = risky, but may start lower.
Use sparingly — only borrow what FAFSA and grants don’t cover.
What Will My Student Loan Payment Look Like?
Before borrowing, it’s smart to estimate what repayment will look like under a standard plan. At CCI Training Center, our financial aid team helps students calculate repayment scenarios based on loan amount, interest rate, and repayment term.
For example, under a 10-year standard repayment plan at roughly 6% interest, the monthly payments would be approximately:
Estimated Monthly Loan Payments (Standard 10-Year Plan)
Loan Balance | Monthly Payment (Approx.) | Total Paid Over 10 Years |
$30,000 | $333 | $39,960 |
$40,000 | $444 | $53,280 |
$50,000 | $555 | $66,600 |
$70,000 | $777 | $93,240 |
Rule of thumb: Every $10,000 borrowed = ~$100/month extra.
CCI Training Center advisors can work with you to explore repayment options, so you understand what your monthly commitment may look like before you borrow.
How to Choose the Best Student Loan Option
Not all loans are equal — making the right choice upfront saves stress later.
- Start with FAFSA → Always secure federal aid first (subsidized if possible).
- Borrow the minimum needed → Cover tuition/fees only; avoid lifestyle borrowing.
- Compare repayment terms → Longer terms lower payments but cost more in interest.
- Check forgiveness eligibility → If you plan to work in government, healthcare, or nonprofits, PSLF may wipe out debt after 10 years.
- Use private loans cautiously → Only if absolutely necessary, and after comparing multiple lenders.
Tip: Federal loans should always be the first choice — they’re safer, cheaper, and more flexible than private loans.
Tips to Reduce Loan Dependence
Even small adjustments can reduce the need for borrowing:
- Apply for multiple scholarships — Even $500 here and there adds up.
- Work part-time or freelance — Cover books, supplies, or living expenses.
- Choose shorter programs — Career training often costs less and takes less time than degrees.
- Buy used or digital textbooks — Save hundreds annually.
- Use tuition payment plans — Spread payments, reduce upfront borrowing.
Even small steps compound over time, helping you graduate with less debt. By stacking strategies, students often cut borrowing by 20–30%, making repayment far easier.
Smart Budgeting Tips for Students
Even if you secure aid, managing money wisely ensures you graduate with less debt. Budgeting can be just as powerful as scholarships.
Here’s a sample monthly budget breakdown for a career training student:
Expense Category | Typical Cost (Monthly) | Savings Strategy |
Housing & Utilities | $800–$1,200 | Share rent with roommates |
Food & Groceries | $300–$400 | Meal prep, bulk buying |
Transportation | $150–$250 | Public transport, carpooling |
Books & Supplies | $100–$200 | Rent or buy used/digital |
Miscellaneous | $100–$150 | Cut subscriptions, budget apps |
Small lifestyle tweaks—like meal prepping or using used textbooks—can save thousands over the course of a program.
Final Thoughts:
Don’t let financial barriers stop you from building the career you deserve. With a mix of federal student loans, grants, scholarships, job training loans, and smart repayment strategies, you can make education affordable.
At CCI Training Center, we’ve helped students for 40+ years by guiding them through FAFSA, financial aid, student loans, and career placement.
Take the next step today:
- Apply for FAFSA with CCI’s help
- Explore student loan options and start training for your future
Education is an investment. Let CCI Training Center help you make it affordable. Reduce Loan Dependence Through Proactive Financial Strategies.
Program Offered
- Pharmacy Technician Training
- Online Medical Assistant
- Medical Billing and Coding Specialist Program
- Cloud Computing Technician Training
- Computer Network Technician
- Business and Accounting
- Radiology Technician Training
- Medical Assistant Program
- Computer Support Technician
- Cybersecurity Program
- Virtual Assistant Training

This article is written by
Share this article
Program Offered
- Pharmacy Technician Training
- Online Medical Assistant
- Medical Billing and Coding Specialist Program
- Cloud Computing Technician Training
- Computer Network Technician
- Business and Accounting
- Radiology Technician Training
- Medical Assistant Program
- Computer Support Technician
- Cybersecurity Program
- Virtual Assistant Training

This article is written by
Share this article
Frequently Asked Questions FAQ's
Does FAFSA cover career training and certificate programs?
Yes. If your school is accredited and Title IV eligible (like CCI Training Center), FAFSA covers Pell Grants and federal student loans.
What’s the difference between financial aid and student loans?
Financial aid includes grants, scholarships, and loans. Loans are just one type — and they require repayment.
How much is the monthly payment on a $30,000 student loan?
On a 10-year plan at ~6% interest, about $333 per month.
Can I use student loans for job training programs or bootcamps?
Yes, if the program is Title IV eligible. Non-accredited bootcamps usually don’t qualify for federal loans but may offer private financing.
Are there income limits for FAFSA eligibility?
No strict limit. Even high-income families qualify for unsubsidized loans. Pell Grants are need-based, but loans are widely accessible.
Can I pay off my student loans early?
Yes. Federal and most private loans have no prepayment penalties. Extra payments reduce interest over time.
Related Articles