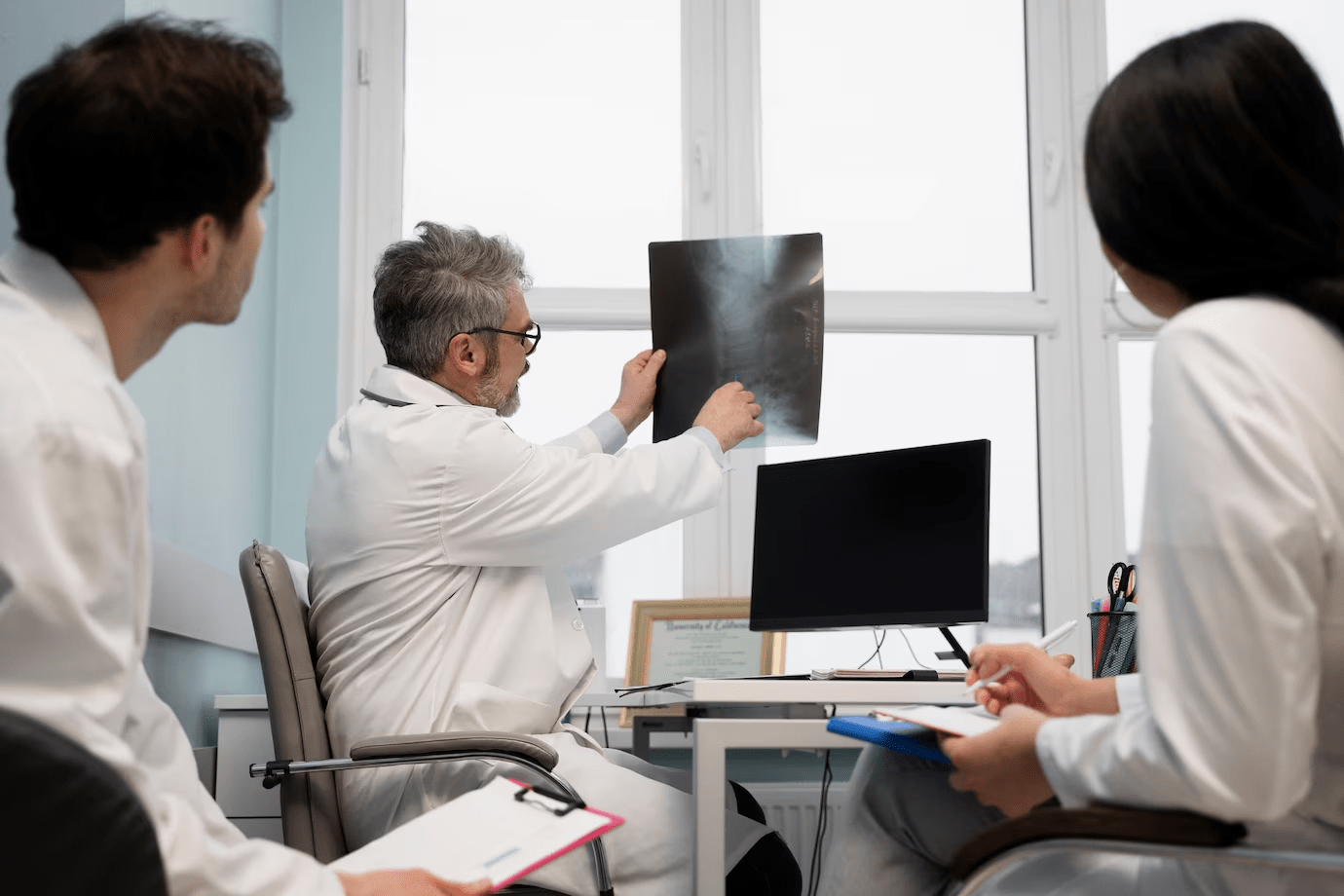
What do Radiologic Technologist (RT) and a Limited Medical Radiologic Technologist (LMRT) do?
Radiologic Technologists (RT):
- Radiologic Technologists, also known as X-Ray Techs, are responsible for operating X-ray machines and other medical imaging equipment.
- They perform a variety of imaging procedures, such as X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans.
- RTs work closely with patients to ensure their safety and comfort during imaging procedures.
- They are trained to position patients correctly to obtain the best images and to follow safety protocols to minimize radiation exposure.
- RTs also work closely with radiologists and other healthcare professionals to review and interpret imaging results.
Limited Medical Radiologic Technologists (LMRT):
- LMRTs are also trained to perform X-ray imaging procedures, but their scope of practice is more limited compared to RTs.
- They typically work in outpatient settings, such as clinics or urgent care centers, where they perform X-rays on patients with specific medical conditions.
- LMRTs are trained to operate X-ray machines and position patients for imaging procedures.
- They are responsible for following safety protocols and ensuring the quality of the images produced.
- LMRTs work under the direct supervision of a licensed physician and may have more limited opportunities for career advancement compared to RTs.
It’s important to note that the specific responsibilities and scope of practice for RTs and LMRTs may vary depending on state regulations and healthcare facility policies.
Where does an RT or LMRT work?
Radiologic Technologists (RT):
- RTs work in a variety of healthcare settings, including hospitals, imaging centers, and physician offices.
- They may specialize in a specific area of radiology, such as mammography, cardiovascular imaging, or interventional radiology.
- RTs often work in collaboration with other healthcare professionals, including radiologists, nurses, and technologists from other specialties.
Limited Medical Radiologic Technologists (LMRT):
- LMRTs primarily work in outpatient settings, such as clinics, urgent care centers, or physician offices.
- They may also find employment in specialized medical practices, such as orthopedic clinics or sports medicine centers.
- LMRTs typically work under the direct supervision of a licensed physician and collaborate closely with other healthcare professionals.
What are the different options for Radiologic Technologists in advancing one’s career?
One of the advantages of pursuing a career as a Radiologic Technologist is the potential for career advancement and specialization. Here are some options for career advancement within the field of radiology:
- Advanced Imaging Modalities: RTs can choose to specialize in advanced imaging modalities such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or nuclear medicine. Specializing in these areas requires additional training and certification.
- Interventional Radiology: RTs can pursue a career in interventional radiology, where they assist radiologists in performing minimally invasive procedures using imaging guidance.
- Radiation Therapy: RTs can specialize in radiation therapy, which involves the use of high-energy radiation to treat cancer and other diseases.
- Radiology Administration: RTs can transition into roles in radiology administration, where they oversee department operations, manage staff, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
These are just a few examples of the many opportunities for career advancement within the field of radiology. Continuing education and specialized training are often necessary to pursue these career paths.
Recommended for you
-
Medical Assistant Program
Take our accelerated Medical Assistant with Clinical Labs program at our Arlington campus and start a new career in as little as 8 months!
Radiology Technician Training
Take our accelerated Radiology Technician Training program at our Arlington campus and start a new career in as little as 8 months!
Medical Billing And Coding Specialist Program
Our 100% online accelerated Medical Billing and Coding Specialist Program makes it possible for you to train for a new career in as little as 25 weeks!
Pharmacy Technician Training Program
Our 100% online accelerated Pharmacy Technician Training program makes it possible for you to train for a new career in as little as 25 weeks!
Online Medical Assistant Program
Our 100% online fast track Medical Assistant program makes it possible for you to train for a new career in as little as 6 months!
What does it take to become an RT or LMRT?
Radiologic Technologists (RT):
- To become a Radiologic Technologist, one must complete an accredited educational program in radiography, which typically results in an associate degree.
- These programs include both classroom and clinical training, providing students with the necessary knowledge and skills to perform imaging procedures safely and accurately.
- After completing their education, aspiring RTs must pass a certification exam administered by the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT) or a similar organization.
- Many states also require RTs to obtain a state license before they can practice.
Limited Medical Radiologic Technologists (LMRT):
- The requirements to become an LMRT may vary by state, as there is no standard national certification for LMRTs.
- Some states may require completion of an accredited educational program, while others may only require on-the-job training or a limited training program.
- LMRTs typically need to pass a state-specific certification exam or meet other requirements set by their state’s regulatory board.
- It’s important to research the specific requirements in your state if you are considering a career as an LMRT.
Final Thoughts
Both Radiologic Technologists (RTs) and Limited Medical Radiologic Technologists (LMRTs) play crucial roles in the field of diagnostic imaging. While RTs have a broader scope of practice and more opportunities for career advancement, LMRTs provide valuable services in outpatient settings under the direct supervision of a licensed physician.
If you are interested in pursuing a career in radiology, it’s important to carefully consider your options and research the requirements in your state. Programs like those offered at CCI Training Center can provide the necessary education and training to become an RT or LMRT. CCI Training Center offers accelerated program formats, flexibility and convenience, instructor-led online classes, instructor support, and career services to help you get started on your career path. Financial aid options are also available to qualified students.
Whether you choose to become a Radiologic Technologist or a Limited Medical Radiologic Technologist, both career paths offer opportunities to make a meaningful impact in the field of healthcare.
Carey Maceira
Related Articles